Pangea Professional Services consist of a flexible and distributed network of systems and data providers which focus on facilitating access to Earth observation data, the principal data sources from one of these systems is a satellite network which constantly generates data from 15 active satellites and give access to historic data of two deactivated ones. 11 of the 15 active satellites have an optical imaging purpose whereas the other 4 have an earth science purpose.
The technology of the active satellites has been developed by an international community including countries like USA, South Korea, France, and China. In general terms, there are 2 types of sensors in satellite monitoring, which are called passive and active. Both are described as follows:
Passive sensors- are those that generate data from radiation reflected from the earth.
Active sensors- are those that emit signals directed to the earth and then generate data on an area of interest.
Passive sensors are those that are already commercially available, their operation is based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation), which are used to detect and classify objects on Earth. This classification can be done at its surface, atmosphere and oceans.
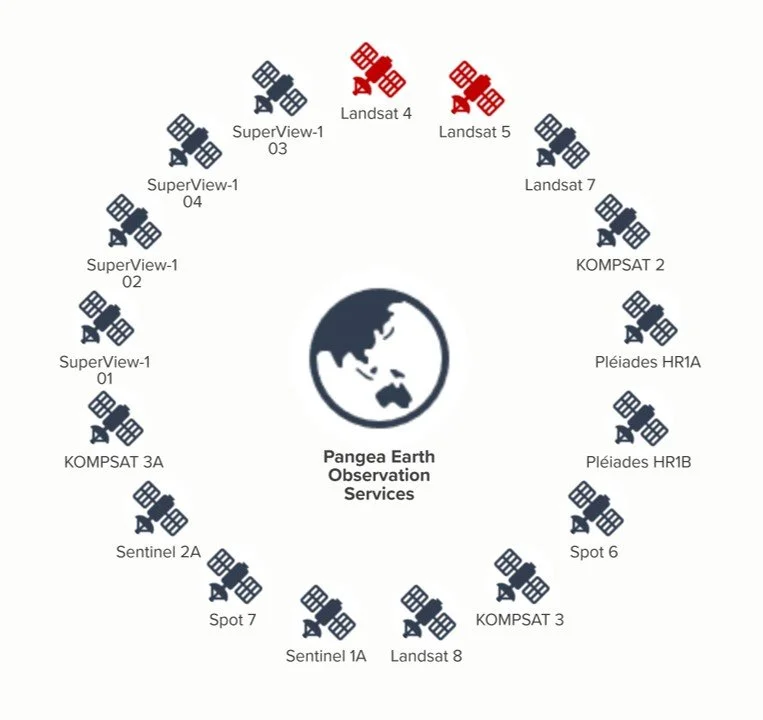
Satellite Network
In a clockwise direction, this diagram shows the selected satellites for data provisioning, sorted by launching year, the satellite network includes the historical data from Landsat 4 y 5 and the continuous data collection from Landsat 7, launched in 1999 up to the latest Super View mission in 2018.
Thematic Mappers
Thematic mappers are simultaneous multi-spectral platforms that take images in multiple wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation (multi-spectral) and are currently being used to prospect for minerals, detect or monitor land usage, detect invasive vegetation, deforestation, and examine the health of indigenous plants and crops, including entire farming regions or particular ecosystems.
Depending on the scope of the observation service, the use cases for thematic mappers can be grouped in two categories.
Land cover- refers to 14 categories of land classified by the observation of physical and biological cover of the Earth’s surface, including natural vegetation and abiotic (non-living) surfaces as per recommendation of the System of Environmental Economic Accounting.
Land use- refers to the set of categories, divisions and classes to classify the activities undertaken for a given area for the purposes of economic production as per recommendation of the System of Environmental Economic Accounting.
Crop monitoring- refers to the data analysis collected by spectral images to forecast yields and minimize effects of climate change.
The available resolution for spectral images pans from 60 meters to 70 centimeters and their frequency varies between every 5 and 2 days, depending on the Geo position of the area of interest.
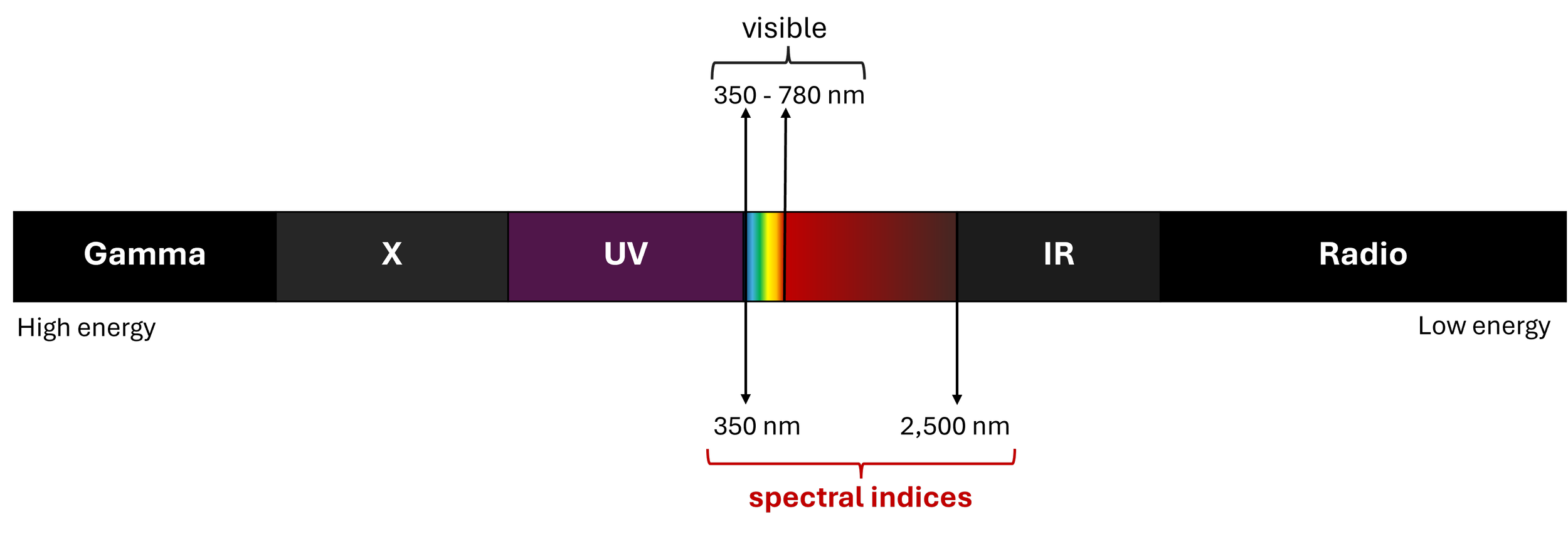
Objects on the Earth’s surface or in its atmosphere tend to have different electromagnetic reflectance/emittance properties, so that the wavelengths measurement makes possible to identify different types of objects based on the spectral signature of targeted objects. The common scale is expressed in nanometers and the best practice is the application of 5 data bands.
The names of the variables within the spectrum vary depending on the satellite mission, however some equivalences can be identified depending on the calculation approach to better describe the properties of an area of interest. There are currently more than 230 sets of equations commonly called indices, of which about 125 are used to describe vegetation conditions on the Earth's surface.